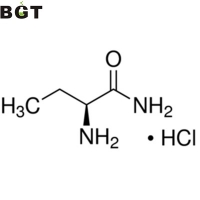
What is L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride?
L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride is a chemical usually used as the chemical reagent and intermediate, such as being the intermediate for Levetiracetam, a medicine resisting epilepsia and convulsions.
Levetiracetam, with the chemical name (S)-2-(2-Oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide, is currently the only epilepsia resisting medicine that has been proven to combine with the synaptin SV2A inside the presynaptic nerve terminal. It can restrain the abnormal electro-discharge in the epilepsia loop, and therefore block the seizures. It is used in the treatment of partial, secondary and general epilepsia.
The structure of Levetiracetam is similar to that of Piracetam. It was manufactured by UCB Pharmaceuticals Inc., a Belgium company. In April 2000, Levetiracetam became available as a generic drug in the United States. Nowadays, it is marketed in many countries as an internationally-recognized new generation broad spectrum epilepsia resisting medicine.
Compared with most other epilepsia resisting medicine, Levetiracetam shows stronger efficacy in resisting epilepsia. Not only its therapeutic index is high, but also its pharmacokinetics property is quite unique. Taken orally, Levetiracetam works fast and is safe. The bioavailability is as high as 100%.
A recent study funded by AgeneBio, supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health, and conducted by Johns Hopkins researchers found out that AGB101, a low-dose version of levetiracetam, works against the memory-robbing ailment, and therefore restores brain function as well as reverses memory loss in early Alzheimer's disease.
Preparation of L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride
Comprising reacting (S)-2-aminobutyric acid hydrochloride with thionyl chloride to form an intermediate, reacting the intermediate with ammonia to form L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride.
Synthesis of Levetiracetam from L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride
Using L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride as the chiral source, the resolution of raceme could be avoided.
A feasible industrialized preparation way for Levetiracetam
Late Ring Closure route
Using L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride as the starting raw material, comprising reacting with SOCl2 and get acyl chloride, and then esterification reacting with methanol or ethanol to get amino ester. Through the intermolecular nucleophilic substitution between amino ester and ethyl-4-bromo butyrate, get an intermediate that after separation and purification, and with the existence of 2-Hydroxy Pyrimidine, get ( S)-PBM by closing loop. Then through the aminolysis reaction, convert the ester into acid amides and get Levetiracetam.
Storage of L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride
L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride should be kept at the temperature of 2-8°C.
The Advantages of BGT for L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride production
Competitive price
We offer the best price on the market due to our advanced process.
Higher purity
Our L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride can reach as high as 99% chemical and optical purity (by HPLC), and is the highest assay that is commercially available. The common purity of L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride on the market is less than 98% chemically and less than 96% optically.
Bulk stock
As L-2-Aminobutanamide hydrochloride is one of Banff’s most important products, a large stock is available all year round.
Others
Safe production process, environmental friendly, sustainable development.